|

Product Links 
|
|

Inside SRI

|
| SRI-Newsletter |
 |
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive monthly specials, manufacturer's feature, and electronics news via email. |
|
 |
|
See Our latest release of SRI-Newsletter here
 |
|
View Our List of Archived Newsletter Articles
 |
|

SRI Links

|
|
Visit our Sister Site,

Distributor of
Industrial Products
| |
|
Web Search ..
Powered by;

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 An arc flash, also called an arc fault or arc blast, is the sudden release of electrical energy through the air when a high-voltage gap exists between conductors. An arc flash gives off thermal radiation (heat) and bright, intense light that can cause burns. Temperatures have been recorded as high as 35,000°F. High-voltage arcs can also produce considerable pressure waves by rapidly heating the air and creating a blast. This pressure burst can hit a worker with great force and send molten metal droplets from melted copper and aluminum electrical components great distances at extremely high velocities. Most 480 V electrical services have sufficient capacity to cause an arc flash hazard. Medium-voltage equipment (above 600 V) is higher potential and therefore a higher risk for an arc flash hazard. Higher voltages can cause a spark to jump, initiating an arc flash without the need for physical contact, and can sustain an arc across longer gaps. Most power-lines use voltages exceeding 1000 volts, and can be an arc-flash hazard to birds, squirrels, people, or equipment such as vehicles or ladders. Arc flashes are often witnessed from lines or transformers just before a power outage, creating bright flashes like lightning that can be seen for long distances.
An arc flash, also called an arc fault or arc blast, is the sudden release of electrical energy through the air when a high-voltage gap exists between conductors. An arc flash gives off thermal radiation (heat) and bright, intense light that can cause burns. Temperatures have been recorded as high as 35,000°F. High-voltage arcs can also produce considerable pressure waves by rapidly heating the air and creating a blast. This pressure burst can hit a worker with great force and send molten metal droplets from melted copper and aluminum electrical components great distances at extremely high velocities. Most 480 V electrical services have sufficient capacity to cause an arc flash hazard. Medium-voltage equipment (above 600 V) is higher potential and therefore a higher risk for an arc flash hazard. Higher voltages can cause a spark to jump, initiating an arc flash without the need for physical contact, and can sustain an arc across longer gaps. Most power-lines use voltages exceeding 1000 volts, and can be an arc-flash hazard to birds, squirrels, people, or equipment such as vehicles or ladders. Arc flashes are often witnessed from lines or transformers just before a power outage, creating bright flashes like lightning that can be seen for long distances.
National Safety Council statistics show that electrical injuries still occur in US industry with alarming frequency:
- 30,000 electrical shock accidents occur each year
- 1,000 fatalities due to electrocution occur each year
Recent studies also indicate that more than half of all fatal electrocutions occurred during routine construction, maintenance, cleaning, inspection or painting activities at industrial facilities. Although electrical shock accidents are frequent and electrocutions are the fourth leading cause of industrial fatalities, few are aware of how little current is actually required to cause severe injury or death. In this regard, even the current required to light just a 7 1/2 watt, 120 volt lamp is enough to cause a fatality - if it passes across a person’s chest.
As the foremost consensus standard for electrical safety in the workplace, NFPA 70E is the primary resource for employers to use in determining how to comply with OSHA’s electrical safety regulations. It is also used by OSHA and the courts in the investigation of injuries in order to assess whether or not the involved employers took reasonable steps and precautions to protect their employees.

Process of Achieving an Electrically Safe Work Condition (120.1)1
- Identify all possible sources of electric supply.
Care should be taken to identify the possible presence of secondary sources.
- Properly interrupt the load current(s) and open the disconnecting device(s).
Not all disconnecting devices are rated to interrupt load currents; this should only be done with a properly rated device.
- Verify deenergization through visual inspection of the disconnect contacts.
Disconnecting means may sometimes fail to open all phase conductors when the handle is operated, so it is necessary to verify physical contact separation. If this requires removing the disconnect door or cover, appropriate PPE must be used.
- Apply lockout/tagout devices.
This should be done in accordance with a formally established company policy.
- Use a voltage detector to test each conductor to which the worker may be exposed in order to verify deenergization.
The voltage detecting device must be functionally tested both before and after taking the measurements in order to ensure that it is working satisfactorily.
- Circuit parts with induced voltages or stored electrical energy must be grounded.
If the conductors being deenergized could contact other energized conductors or circuit parts, grounding devices rated for the available fault duty should be applied.
According to both CSA and NFPA 70E standards, an arc flash hazard analysis shall be done in order to protect personnel from the possibility of being injured by an arc flash. As part of this analysis, flash protection boundaries must be determined based on available bolted fault currents and the incident energy exposure level for personnel working within this boundary must be calculated.
Personal and Other Protective Equipment (PPE)

Employees working in areas where electrical hazards are present shall be provided with, and shall use, protective equipment that is designed and constructed for the specific part of the body to be protected and for the work to be performed.
Requirements for eye, hand, head and body protection and/or v-rated tools are determined based on the hazard/risk category for the work to be performed. The standard provides a reference table indicating the hazard/risk category for many of the electrical tasks performed in industry and also provides a chart showing the protective equipment that is required for each hazard/risk category.
Provide the Safety of a Switch with Every Plug and Receptacle
Meltric’s Decontactor Series switch-rated plug and receptacles combine the safety and functionality of a disconnect switch with the convenience of a plug and receptacle. They allow users to safely make and break connections under full load and provide significant protection in overload and short circuit conditions. Decontactors are UL and CSA rated for:
- Branch circuit disconnect switching, up to 200A
- Motor circuit disconnect switching, up to 60 hp
- Short circuit closing and withstand, up to 100kA in circuits protected with RK1 current limiting fuses
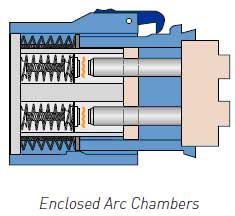
Meltric’s Decontactor Series switch-rated plugs and receptacles simplify compliance with NFPA 70E by eliminating the possibility of exposure to energized parts and arcing when making and breaking the electrical connections required to change-out motors and other equipment. This avoids the need to take many of the special precautions required to ensure that workers are
aware of and protected from the shock and arc-flash hazards that exist whenever work is performed on or around energized circuit components. With push button load-breaking, UL and CSA switch ratings for applications up to 200A and short circuit closing and withstand ratings up to 100kA (in circuits protected with RK1 current limiting fuses). Decontactors provide a safe, simple and convenient means of disconnecting the load. There is no need for the interlocks and auxiliary disconnects required with standard plugs and receptacles.
- https://www.osha.gov/grant_materials/sh-1661507/arc_flash_handout.pdf
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arc_flash
- Electrical Injuries: Engineering, Medical, and Legal Aspects By Robert E. Nabours, Raymond M. Fish, Paul F. Hill -- Lawyers and Judges 2004 Page 96
|
**Specifications subject to changes**
|
|
 |
|

Product Spotlight
 |
|

Sponsored Ads
 |
|